Varicocele Embolisation
Varicocele embolisation is a non-invasive treatment option used to treat enlarged veins in a scrotum, known as a varicocele. It diverts the blood away from the enlarged vein, allowing it to return to it's usual size. It’s a very safe treatment, usually preferred over surgery thanks to its reduced risk and side effects.
What is Varicocele Embolisation?
Varicocele embolisation is, put simply, a medical procedure of blocking blood vessels in the testicles that have become enlarged, known as a varicocele. The process is minimally invasive, very safe, and performed by a specialist known as an interventional radiologist.
An Interventional Radiologist, a specially trained medical professional who combines expert training in imaging (x-rays, ultrasounds, CTs and MRIs) with minimally invasive treatment options, uses blocking agents to divert blood flow away from the enlarged vein in the scrotum that has caused the varicocele and help improve symptoms.
Embolisation is used to treat a wide variety of conditions and is considered extremely safe. It has been used for decades for both elective and emergency procedures to help stop blood flow.
It is highly targeted and minimally invasive, making it an excellent option if you are troubled by your varicocele but do not want surgery. It does not involve any incisions or cuts on the groin or scrotum and does not need a general or spinal anesthetic.
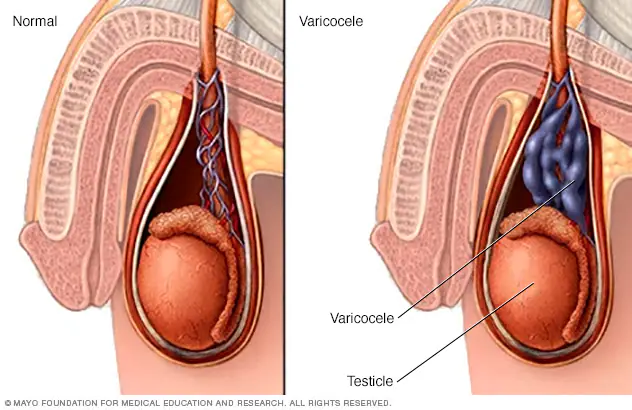
What is a Varicocele?
A varicocele is a collection of swollen veins in the scrotum and is quite common - a condition that occurs in approximately 15-25% of young men.
Varicoceles develop because of a problem with the valve in the veins that carry blood away from the scrotum and testicles.
A spermatic cord, within the pampiniform plexus, holds up each testicle, and this cord contains the veins, arteries, and nerves that support the testicles. In healthy veins, one-way valves move the blood from the testicles back to the heart.
When "leaky", these valves do not return the blood back to the heart as they should and this causes a buildup of pressure, and therefore swollen veins, and a varicocele develops slowly over time.
Usually, it only causes minor symptoms such as a small aching in the scrotum or groin, swollen veins visible to the naked eye, or testicular atrophy (one testicle is smaller than the other). In some cases, though, the symptoms are more severe and can impact everyday life.
Varicoceles can also be associated with reduced fertility and are therefore commoner in those men suffering from fertility problems.
How is Varicocele Embolisation Performed?
- Varicocele Embolisation is performed by an Interventional Radiologist (IR) in an operating room or suite. It is usually performed on an outpatient basis given the quick nature of the procedure and recovery. In some cases, though, you may need hospital admission and your IR will inform you of this during your consultation.
- To begin with, you’ll be given a mild sedative, usually via an intravenous (IV) line, to help you relax, and you’ll also receive a local anesthetic on the inner part of your thigh or groin.
- A small incision is made where you have received the anesthetic, in which a needle will be inserted to access a major vein. Your IR will then insert a catheter tube into this vein.
- Throughout the procedure, your IR will use imaging techniques to help them ‘see’ what they are doing and to assist in moving the catheter tube to the correct location.
- Once the tube is in place at the varicocele, a small coil or a special liquid is released into the affected vein. This is called a blocking agent and is used in all forms of embolisation to block or divert the blood flow from the affected area.
- Once complete, the catheter is removed, the incision is closed, and a bandage placed over the entry area.
- The whole procedure is usually completed within one hour.
What are the Risk and Benefits of Varicocele Embolisation?
Just like any medical procedure, varicocele embolisation comes with its own set of risks and benefits, however, varicocele embolisation is considered a very safe treatment option. Your doctor can explain the benefits and risks to you in detail during your consultation, and they include:
Benefits of Varicocele Embolisation
- No surgical incision - a small nick is all it takes, and it doesn’t require stitches.
- The recovery time is much shorter - usually 1-2 days for embolisation compared with 2-3 weeks for surgery.
- 90% success rate
Risks of Varicocele Embolisation
- Infection - the chance of infection is less than 1 in 1000
- Allergic reaction
- Risk of bleeding or damage to the blood vessels caused by the catheter
- Movement of the blocking agent used to block the enlarged vein
- Lower back pain, inflammation of the scrotum, inflammation of the vein, and nausea
- Failure of the procedure and your varicocele returning
- Personal factors based on your specific health profile
How Long After Varicocele Embolisation Does Sperm Improve?
One study found that sperm parameters (number, shape and movement) improved after 3 months of having a varicocele repaired.
How Long After Varicocele Embolisation Can We Get Pregnant?
A study in 2011 found that once a varicocele is repaired, the average time for spontaneous pregnancy is 7 months.
Recovering from Varicocele Embolisation
Recovery from varicocele embolisation is usually very short. You’ll be monitored for a while after your procedure and can usually go home the same day (at Northern Beaches Interventional Radiology, all our procedures are performed in the morning, greatly improving your chances of returning home the same day).

You’ll be able to return to work the following day (depending on your job) and you should avoid heavy lifting for about a week, and avoid sexual activity for a couple of weeks.
For men who have undergone varicocele embolisation to improve fertility, how long after the procedure until sperm improves can vary, but in general, you can expect it to take up to 3 months before you see an improvement, as new sperm takes 3 months to develop. Your fertility specialist will be able to give you more detailed advice and information.
You’ll have a follow-up consultation with us after 2 weeks to check on your recovery and ensure the procedure was a success. If your treatment was due to infertility, you’ll also follow up with your fertility specialist for a semen analysis.
How Much Does Varicocele Embolisation Cost?
It depends. When we meet with you for a consultation we can discuss the cost and payment of the procedure with you. Your out of pocket costs will depend on a few variables, including whether or not you have private health insurance.
Do I Need My Varicocele Treated?
For most men with a varicocele, treatment is not required. Since varicoceles usually don’t have any symptoms they can be left alone. If there is concern over your fertility then treatment becomes more important. If it is causing pain or discomfort you may also want to have it treated.
Varicoceles cannot be treated with medication, nor is there any way to prevent them. Surgery is an option, but it is not the only option - this is where the minimally invasive, non-surgical option of varicocele embolisation comes in.
Am I a Candidate?
Varicocele embolisation is not the only option - some men prefer to have surgery. This is because a varicocele embolisation involves a small incision in the groin and has a very slight chance of damaging the tube that carries sperm from the testicle.
Let’s Discuss Your Treatment Plan
Discussing your diagnosis with your GP or Interventional Radiologist will help decide the best treatment option for you. If you’ve been diagnosed with varicocele, or are experiencing some symptoms, you can book a consultation with us and we’ll discuss your treatment options with you.
Safe, effective treatments with less pain and quicker recovery.
Ensure you know all your options prior to invasive surgical treatment, schedule a consult with Dr Shaun Quigley.


